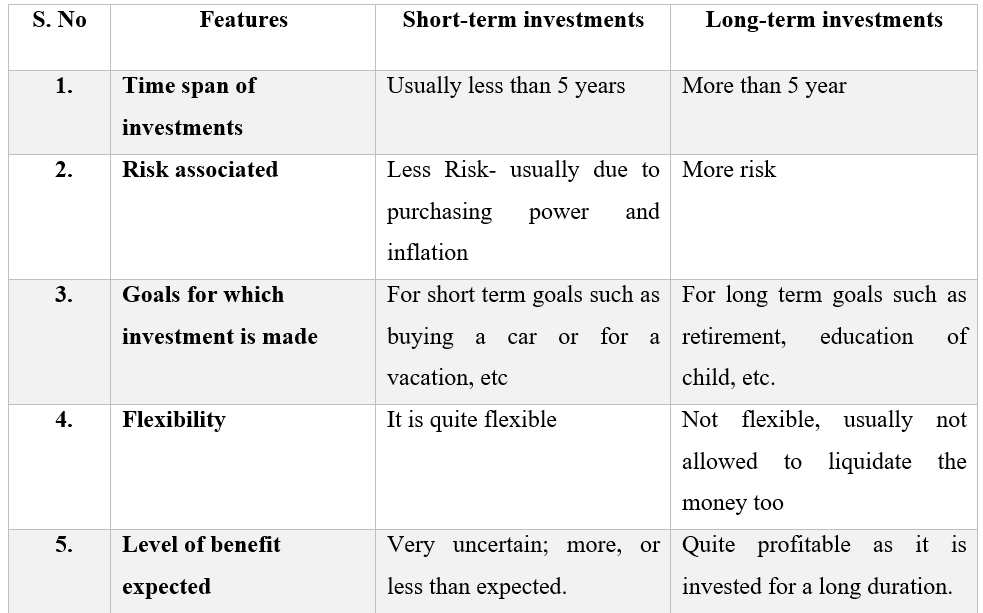
Investing your money can be a smart move to grow your wealth, but with so many options out there, it’s important to understand the differences between short-term and long-term investments. Short-term investments typically refer to those that last for less than five years, while long-term investments involve holding onto an asset or investment for longer periods, often over five years. In this article, we will explore the distinctions between these two types of investments and help you make informed decisions for your financial future. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out, this article will provide you with valuable insights and practical advice on navigating the world of investing.
This image is property of stashlearn.wpengine.com.
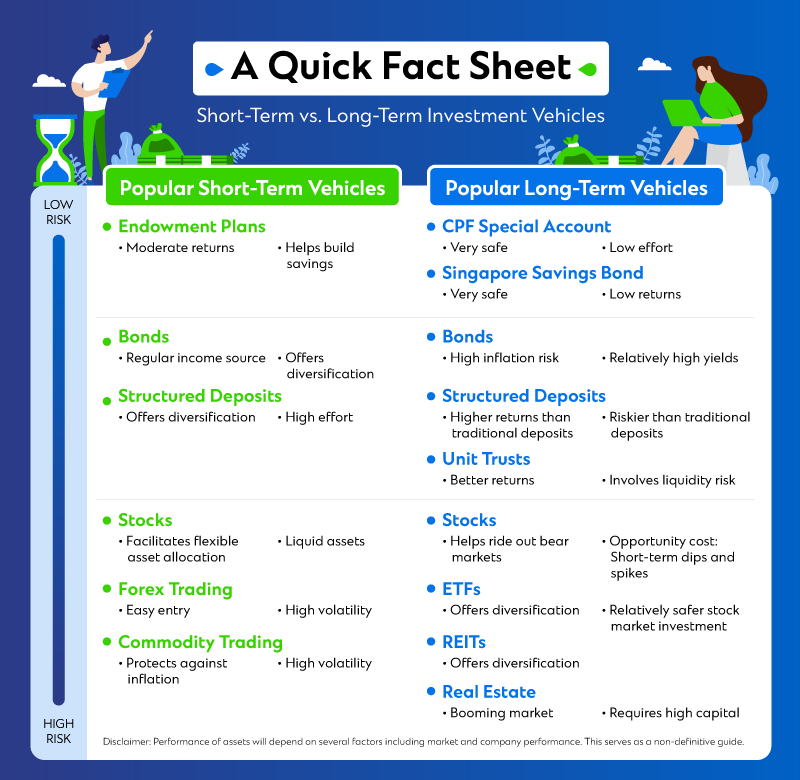
Short-term Investments
Definition
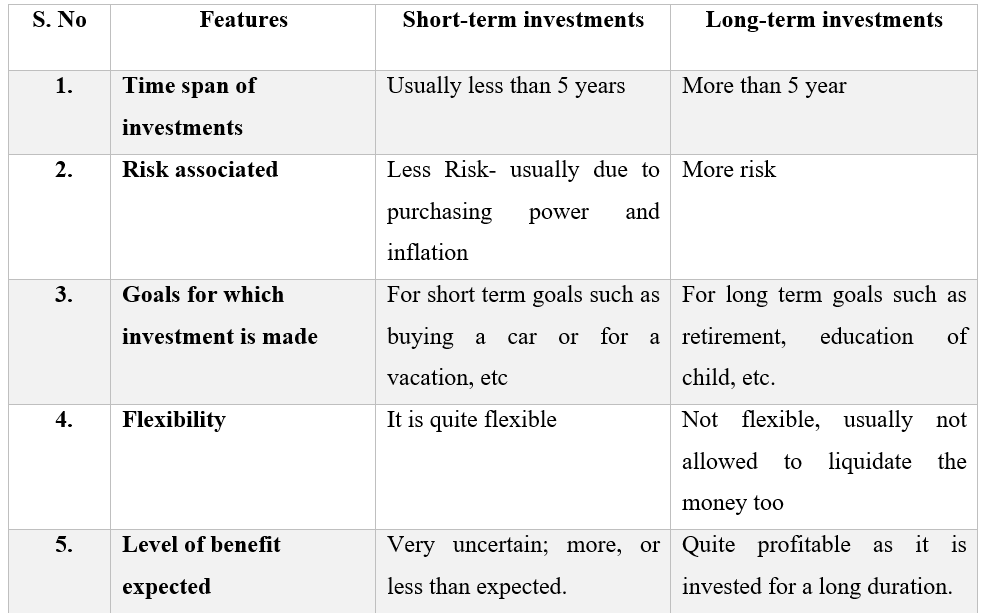
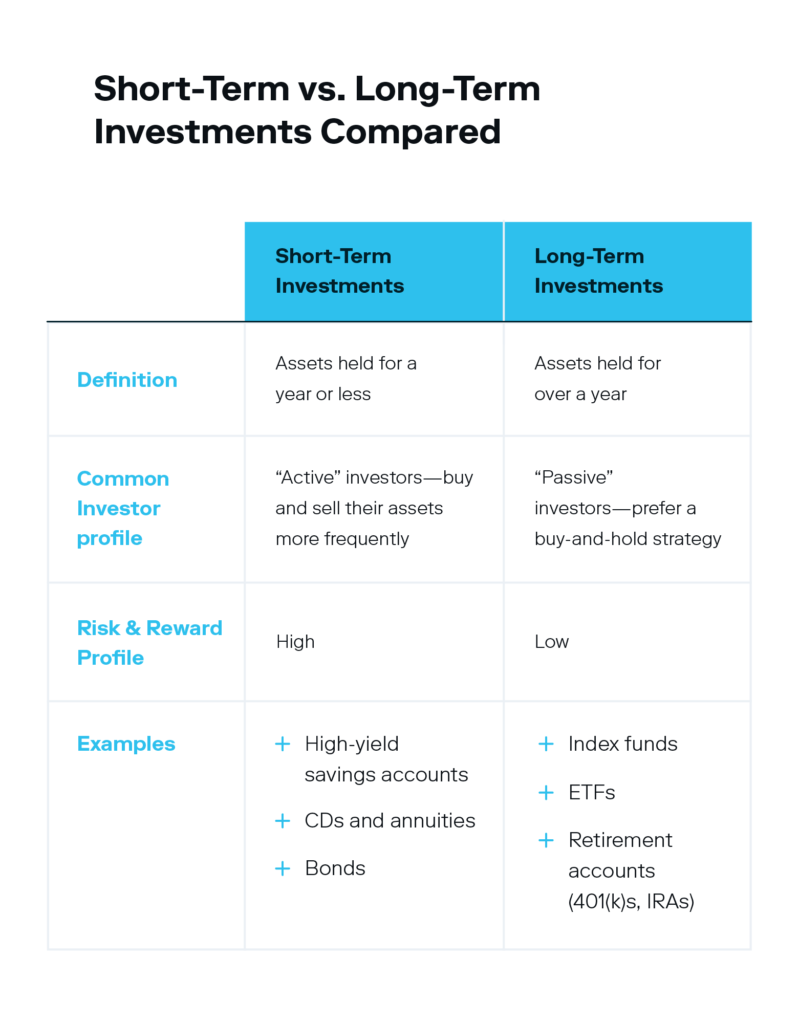
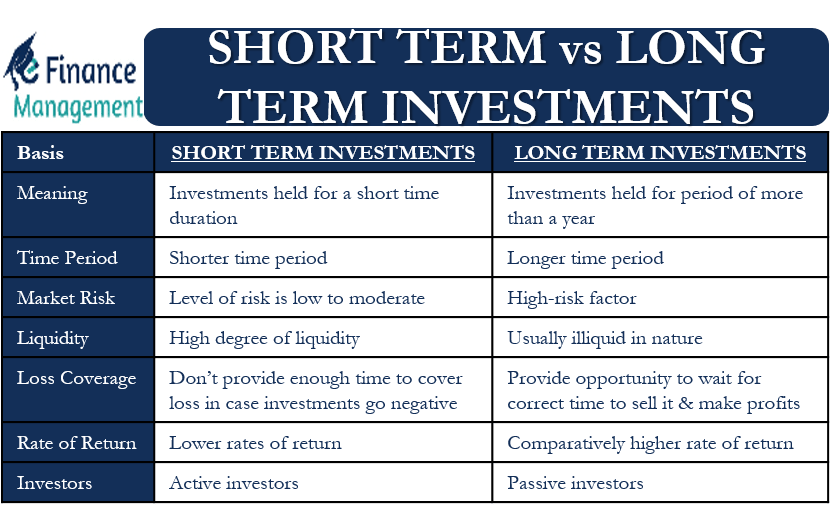
Short-term investments refer to financial assets that are intended to be held for a relatively short period of time, typically one year or less. These investments are considered to be more liquid than long-term investments, meaning they can be easily converted into cash without significant loss of value.
Time Horizon
The time horizon for short-term investments is relatively short, typically ranging from a few weeks to a year. These investments are often used to meet short-term financial goals or to preserve capital while awaiting more favorable investment opportunities.
Risk
Short-term investments generally carry lower risk compared to long-term investments. This is because the shorter time horizon allows investors to avoid prolonged market fluctuations and potential losses that may arise in the long run. However, it is important to note that short-term investments are not entirely risk-free. They are still subject to market volatility and economic conditions.
Returns
Short-term investments usually offer lower returns compared to their long-term counterparts. This is because the goal of short-term investing is to preserve capital and meet immediate financial needs rather than to achieve significant growth.
Examples
Some common examples of short-term investments include savings accounts, certificates of deposit, money market accounts, and treasury bills. These options offer relative stability and quick access to funds, making them suitable for short-term financial goals and emergencies.
Long-term Investments
Definition
Long-term investments are financial assets that are intended to be held for an extended period of time, typically exceeding one year. These investments are focused on achieving long-term financial goals, such as retirement planning, purchasing property, or funding education.
Time Horizon
Long-term investments have a significantly longer time horizon compared to short-term investments. The extended timeframe allows for potential growth through compounding and the ability to ride out market volatility. Investments in this category are expected to be held for several years or even decades.
Risk
Long-term investments carry a higher level of risk compared to short-term investments. The prolonged time horizon exposes investors to market fluctuations, economic downturns, and other risks that may impact the value of their investments. However, over the long term, well-diversified portfolios have historically shown resilience and the potential for higher returns.
Returns
Long-term investments have the potential to generate higher returns compared to short-term investments. This is due to the opportunity for compound growth and the ability to weather short-term market fluctuations. Over a longer period, investments in assets such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and mutual funds have the potential to appreciate in value and provide substantial returns.
Examples
Common examples of long-term investments include stocks, bonds, real estate, and mutual funds. These options offer the potential for capital appreciation and income generation over an extended period. Long-term investors often take advantage of market trends and utilize strategies to maximize returns while managing risk.
This image is property of efinancemanagement.com.
Factors to Consider
Investment Goals
When deciding between short-term and long-term investments, it is essential to consider your investment goals. Define your financial objectives and determine the time frame in which you aim to achieve them. Short-term investments are suitable for immediate financial needs or preserving capital, while long-term investments are more aligned with goals that require growth and accumulation of wealth over an extended period.
Risk Tolerance
Your risk tolerance is another critical factor to consider when choosing between short-term and long-term investments. Short-term investments generally carry lower risk since they are not exposed to prolonged market volatility. On the other hand, long-term investments involve a higher level of risk due to market fluctuations. Assess your risk tolerance based on your financial situation, comfort level with potential losses, and your investment timeframe.
Liquidity Needs
Evaluate your liquidity needs when making investment decisions. Short-term investments offer more immediate access to funds compared to long-term investments. If you anticipate the need for quick cash or an emergency fund, short-term investments such as savings accounts or money market accounts may be more suitable. However, if you have a long-term horizon and can afford to tie up your funds, long-term investments like stocks or real estate may offer greater potential returns.
Market Conditions
Consider the prevailing market conditions and economic outlook when choosing between short-term and long-term investments. Short-term investments may be preferred during periods of high market volatility or uncertainty. On the other hand, long-term investments tend to be more favorable during periods of economic growth and stability. Keep an eye on market trends and consult with a financial advisor to make informed investment decisions.
Tax Implications
Tax implications should also be taken into account when deciding between short-term and long-term investments. Short-term investments are typically subject to ordinary income tax rates, while long-term investments are generally eligible for lower capital gains tax rates. Consult with a tax professional or financial advisor to understand the tax implications of different investment options and how it aligns with your overall tax strategy.
Short-term Investment Options
Savings Accounts
Savings accounts are one of the most common short-term investment options. They offer a secure place to store your money while still earning interest. Savings accounts are highly liquid, allowing you to withdraw funds at any time without penalty. While savings accounts may provide relatively low interest rates compared to other short-term investments, they are considered to be low risk.
Certificates of Deposit
Certificates of Deposit (CDs) are time deposits offered by banks that provide a fixed interest rate and a specified maturity date. CDs usually have a higher yield compared to savings accounts but require a fixed term commitment. The funds invested in a CD cannot be withdrawn before the maturity date without incurring penalties. They are a suitable option for individuals seeking a conservative short-term investment with fixed returns.
Money Market Accounts
Money market accounts are short-term investment vehicles that combine features of savings accounts and certificates of deposit. These accounts typically offer higher interest than regular savings accounts while providing check-writing capabilities. Money market accounts may also come with certain restrictions, such as minimum balance requirements or limited monthly transactions.
Treasury Bills
Treasury bills, also known as T-bills, are short-term government debt securities issued by the U.S. Treasury. They are considered to be one of the safest forms of investment due to their backing by the U.S. government. T-bills have maturities of one year or less and are sold at a discount to their face value, with the difference representing the interest earned. They are highly liquid and can be easily bought and sold in the secondary market.
This image is property of av.sc.com.
Long-term Investment Options
Stocks
Stocks represent ownership in a company and can be a long-term investment option suitable for investors seeking capital appreciation. By purchasing shares of stock, you become a shareholder and participate in the company’s growth and profitability. Stocks offer the potential for higher returns but also involve greater risk due to market volatility.
Bonds
Bonds are debt instruments issued by governments, municipalities, and corporations to raise capital. They are considered safer than stocks since they provide fixed interest payments and return of principal upon maturity. Bonds can offer regular income streams and are commonly used by long-term investors seeking stable returns.
Real Estate
Investing in real estate can be a long-term strategy for building wealth. Real estate investments can include rental properties, residential or commercial properties, and real estate investment trusts (REITs). When held for the long term, real estate has the potential to appreciate in value and generate regular income from rent.
Mutual Funds
Mutual funds pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other assets. They offer a convenient way for individuals to access professional investment management and diversification, making them suitable for long-term investors with varying risk tolerances. Mutual funds can provide exposure to different asset classes and sectors, allowing for potential growth over time.
Benefits of Short-term Investments
Flexibility
One of the key benefits of short-term investments is their flexibility. Short-term investments can easily be liquidated or transferred into other investments, allowing for adjustments to align with changing financial goals or market conditions. This flexibility enables investors to take advantage of new opportunities or respond to unexpected financial needs.
Quick Access to Funds
Short-term investments provide quick access to funds when needed. Savings accounts, certificates of deposit, and money market accounts can often be accessed without penalty, allowing for immediate cash availability. This convenience makes short-term investments suitable for financial goals that require access to funds in the near future or for emergencies.
Lower Risk
Short-term investments generally carry lower risk compared to long-term investments. The shorter time horizon reduces exposure to market volatility and potentially drastic economic changes. With lower risk comes a greater level of stability, providing peace of mind for investors who have conservative risk tolerance or short-term financial needs.
This image is property of s3.ap-south-1.amazonaws.com.
Benefits of Long-term Investments
Potential for Higher Returns
One of the primary benefits of long-term investments is the potential for higher returns compared to short-term investments. The extended time horizon allows for the power of compounding and the ability to weather market volatility. Over the long term, investments in assets such as stocks, bonds, and real estate have historically shown the potential for growth and substantial returns.
Compound Growth
Long-term investments benefit from the concept of compound growth. Compounding occurs when the returns earned on an investment are reinvested, generating additional returns over time. This compounding effect can significantly enhance investment growth, especially when reinvested returns are compounded year after year.
Diversification
Long-term investments often involve diversification, spreading investments across various assets to minimize risk. This diversification helps reduce the impact of individual investments and promotes a more stable portfolio. By diversifying across different asset classes, sectors, and geographic regions, long-term investors can potentially achieve a more balanced risk-return profile.
Drawbacks of Short-term Investments
Lower Returns
One of the main drawbacks of short-term investments is their relatively lower returns compared to long-term investments. The focus of short-term investing is on capital preservation and meeting immediate financial needs, rather than maximizing long-term growth. Investors seeking significant wealth accumulation may find that short-term investments do not provide the desired return on investment.
Inflation Risk
Short-term investments may be susceptible to inflation risk. If the rate of inflation exceeds the returns earned on short-term investments, the purchasing power of those investments may erode over time. Inflation can reduce the real value of returns and potentially impact the ability to meet long-term financial goals.
Missing Out on Market Upside
Short-term investments may limit an investor’s participation in potential market upside. By holding investments for shorter periods, investors may miss out on extended periods of market growth and the opportunity for substantial returns. While short-term investments provide stability, they may not capture the full potential of long-term market gains.

This image is property of av.sc.com.
Drawbacks of Long-term Investments
Market Volatility
One of the main drawbacks of long-term investments is their exposure to market volatility. Investments held over extended periods may experience significant fluctuations in value due to economic conditions, market cycles, or unforeseen events. Investors must be prepared to endure short-term losses and have a long-term perspective to ride out market volatility.
Lack of Liquidity
Long-term investments are typically less liquid compared to short-term investments. Assets such as real estate or certain types of funds may require time and effort to sell or liquidate. If an investor needs access to funds quickly, they may face challenges in converting long-term investments into cash without significant transaction costs or delays.
Potential for Losses
Long-term investments carry the risk of potential losses. Market downturns, economic recessions, or changes in financial conditions can significantly impact the value of long-term investments. Investors need to carefully assess their risk tolerance and ensure they have a diversified portfolio to mitigate potential losses and minimize their impact.
Balancing Short-term and Long-term Investments
Asset Allocation
A critical aspect of balancing short-term and long-term investments is proper asset allocation. By diversifying investments across different asset classes and investment horizons, individuals can spread their risk and potentially achieve both stability and growth. Asset allocation should be based on financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon, and should be regularly reviewed and adjusted as needed.
Dollar-Cost Averaging
Dollar-cost averaging is a strategy that involves regularly investing a fixed amount of money into investments over a prolonged period. This approach can help mitigate the impact of market volatility since you buy more shares or units when prices are low and fewer when prices are high. Dollar-cost averaging is a popular technique to balance short-term and long-term investments, allowing investors to take advantage of market fluctuations without the need for precise market timing.
Rebalancing
Regularly rebalancing your investment portfolio is essential to maintain the desired allocation between short-term and long-term investments. Over time, the relative values of different investments may change, impacting the risk profile and overall balance. By periodically reviewing and rebalancing your portfolio, you can ensure that your investments align with your goals and risk tolerance.
Investment Planning
Comprehensive investment planning is crucial for balancing short-term and long-term investments. This includes setting clear financial goals, understanding risk tolerance, and developing a well-defined investment strategy. Seek the guidance of a financial advisor to create a personalized investment plan that considers your unique circumstances and helps you achieve both short-term and long-term financial objectives.
In conclusion, choosing between short-term and long-term investments involves considering factors such as investment goals, risk tolerance, liquidity needs, market conditions, and tax implications. Short-term investments offer flexibility, quick access to funds, and lower risk, while long-term investments provide potential for higher returns, compound growth, and diversification. It is important to balance short-term and long-term investments through suitable asset allocation, dollar-cost averaging, regular portfolio rebalancing, and comprehensive investment planning to achieve a well-rounded and successful investment strategy.